| Colors | HEX Code | RGB | CMYK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | #032EA1 | 3, 46, 161 | 98, 71, 0, 37 |
| Red | #E00025 | 224, 0, 37 | 0, 100, 83, 12 |
| White | #FFFFFF | 255, 255, 255 | 0, 0, 0, 0 |
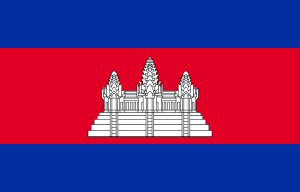
The Cambodian Flag has three horizontal stripes. The upper and lower stripes are blue, while the middle stripe is twice as wide as the blue stripes. In the middle of the red stripe, there is a three-towered temple featured in white, and representing Angkor Wat, a Hindu-Buddhist temple complex in Cambodia, silhouetted in black.
Meaning of the Cambodian Flag
The blue color in the Cambodian flag represents the monarchy, while the red color represents the nation’s courage and determination. The temple in the center of the flag represents the culture and history of the country.
History of the Cambodian Flag
Cambodia had a yellow triangular flag with a green border before it became a French protectorate in 1863. The flag was similar to the current flag of Cambodia. In 1941, the Japanese took control of Cambodia and changed the flag. When the Japanese occupation ended in 1945, the old flag of the French protectorate was reintroduced. Cambodia proclaimed its independence from France in 1953, and the flag remained the same till 1970. The country was led by a republican government that followed a military coup, and the country’s name became the Khmer Republic. The flag of the Khmer Republic was a blue field, with a red canton on which the Angkor Wat was featured in white, and three five-pointed stars were placed on the upper side next to the canton. The flag was changed again in 1975 when the Red Khmer took control, and then in 1979 when Vietnam occupied Cambodia and changed the name of the country again to the People’s Republic of Kampuchea. In 1989 the flag returned to the red and blue stripes, but the Angkor Wat was featured in yellow. In 1992, the United Nation administered Cambodia, and a blue flag with a white map of the country was adopted. Finally, in 1993, the original flag was re-adopted, and is still in use till today.